A review of the hottest 2013 proxy issues plus a preview of the likely trends for 2014
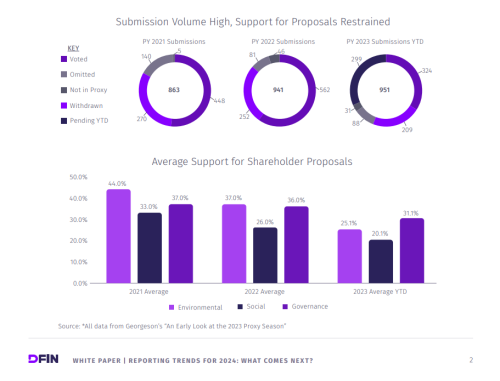
The 2013 proxy season was noteworthy for a sea change in shareholder engagement by companies. The main catalyst was increased resolve by firms to secure majority support among shareholders for their say-on-pay proposals. Support levels for say-on-pay proposals among companies in the S&P 1500 index rose to an average 90.3 percent from an average 88.6 percent in 2012. Here we look at trends from the past proxy season and detail some issues to watch for in 2014.
What’s in
Shareholder engagement
There has been a dramatic jump over the last few years in the number of companies willing to engage with shareholders. Institutional investors have been overwhelmed with issuers’ requests for meetings or discussions, many of which are focused on say on pay. Smaller companies tend to concentrate their efforts on their top 10-25 shareholders, while campaigns for larger firms tend to be more involved, sometimes extending as far as their largest 150 shareholders, says Steven Pantina, managing director of proxy solicitor Georgeson.
‘The expansive growth in the scope, length and breadth of outreach campaigns is a really notable event in the proxy world,’ he observes. ‘It’s no longer just one call 10 days prior to the meeting. The amount of time companies are willing to invest to ensure their message is being received and to work through issues is very significant compared with recent years.’ There has also been much greater effort by companies to settle any proxy contests before a shareholder vote, he adds.
In expanding their outreach to smaller investors, companies need to understand that mid-sized fund managers generally lack the resources of larger investors, which can afford dedicated governance research teams. That forces smaller investors to be selective when engaging with companies, says Amy Borrus, deputy director at the Council of Institutional Investors (CII). ‘That’s also why companies have to make sure their disclosures are top-notch, because it may be as close as they get to talking to smaller investors,’ she notes.
Voting against directors
There was a big push in 2013 by activist investors to force changes on boards, with Hess, Occidental Petroleum, Hewlett-Packard and JPMorgan Chase serving as the most prominent examples. A board shake-up at JPMorgan Chase occurred despite majority support for three members of the board’s risk committee standing for re-election in May. Two months later, two of those directors resigned, having taken heat for risk oversight lapses that facilitated a $6 bn trading loss in London and other problems at the bank.
‘Shareholders used to be reluctant to vote against directors, but that’s no longer the case,’ says Borrus. ‘They’re increasingly willing to hold directors to account for poor oversight.’
The number of proxy contests has risen steadily from nine in 2010 to 15 in 2012 and 19 in 2013. The proliferation of proxy contests has also brought an increase in alternative slates of directors proposed by activist investors.
In 2014 there is likely to be increased assessment of directors’ performance, with a particular focus on director tenure, says Hank Boerner, chairman of the Governance & Accountability Institute. He believes directors’ communication with shareholders, which has been restricted until now, will also draw more attention. ‘We will see some interesting models emerge as companies explore how to do this,’ he predicts.
Executive pay and majority voting
There has been a notable decline in executive compensation-related proposals from a few years ago as the issue has been addressed in the Dodd-Frank legislation, notes Pantina. Today, two kinds of proposals dominate this category: those seeking to eliminate accelerated vesting in change-of-control agreements, and those seeking equity retention requirements for CEOs and named executive officers. Combined, these two issues account for 60 of the 83 executive pay proposals that appeared on proxy ballots this year, according to Georgeson’s 2013 annual corporate governance review. Overall, however, executive pay-related proposals are down this year from 116 in 2010.
Equity retention and accelerated vesting proposals have become popular among shareholder ctivists as investors ‘seek ways to ensure shareholders’ interests and management’s interests are more closely aligned,’ says Pantina, co-author of Georgeson’s review.
Meanwhile, Borrus expects to see more majority voting in uncontested director elections. With 80 percent of S&P 500 companies having adopted it in their bylaws, the focus is shifting to small and mid-caps. Average support for shareholder proposals advocating a switch to majority voting rose to 58 percent in 2013 from 44 percent in 2005. In June the CII petitioned three major stock exchanges to make majority voting a listing requirement for public companies.
Declassifying boards and proxy access risk
The demand that companies destagger board elections is among the most popular issues shareholder activists are pursuing, and one Pantina expects to continue in the years ahead. Still, the number of proposals seems to have spiked and dropped precipitously in alternate years since 2009, when 43 proposals asked companies to repeal their staggered boards. This year, the number of proposals dropped to 23 due to fewer targets. Meanwhile, management proposals to declassify boards jumped to 60 in 2013 from 41 in 2012, after hovering between 29 and 46 proposals over the past nine years, according to Georgeson data.
Now that shareholders are able to seek proxy access, some observers had expected this to be a boom issue with explosive growth due to interest by shareholder activists, but that hasn’t materialized, says Pantina. A federal court ruling forcing the SEC to discard a rule that would have allowed for proxy access has left individual firms to decide for themselves what the ownership and holding duration criteria should be for shareholders to qualify to add director nominees to the proxy ballot.
What’s out
Poison pill proposals
The popularity of shareholder proposals asking companies to redeem their poison pills has plummeted in recent years as a result of so many companies either proactively redeeming poison pills or choosing not to renew them upon their natural expiration, says Pantina. This year there were no poison pill proposals, compared with three proposals last year and one proposal in each of the two immediately prior years.
Cumulative voting for directors
Calls for cumulative voting – which allows shareholders to distribute votes for directors up for re-election in any proportion they like – are on the decline as well, according to Pantina. The lack of restriction as to how votes are distributed enables investors to concentrate all their votes on the one or two particular directors they most strongly favor. The sole cumulative voting proposal filed in 2013 received just 26 percent support compared with the average 25 percent support that 11 such proposals received in 2012 and the 33 percent average support for 22 proposals in 2011.
Mounting demand for majority voting in uncontested director elections is eclipsing interest in cumulative voting because the two initiatives don’t work well together, Pantina points out. Because cumulative voting increases the likelihood of individual directors failing to receive a majority of votes cast, it ‘has become the lesser issue and has fallen by the wayside,’ he concludes.
This article also appears in the December issue of Corporate Secretary.
|
Questions about pay ratio rule persist |
|
Proxy access demands will continue in 2014 |
|
Be prepared to fight activists
|
|
Threats from hedge funds loom large |